More than a set of closed functionalities for public debt management, the solution developed by QUIDGEST, based on automatic code generation and modeling, guarantees easy adaptation to debt management structures and instruments, a flexible and adjustable approach to the requirements of each reality and each moment.
PDMS –
PUBLIC DEBT MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
It’s an instrument for sustainable public debt management, according to international guidelines and policies, particularly relevant for Low-Income Countries (LIC), with the ability to respond effectively to operational needs and to define scenarios and strategies for the future, within the controlled risk.
Quidgest’s solution for Public Debt Management, PDMS (Public Debt Management System) has been specifically designed to meet the operational and strategic debt management needs. The PDMS’s mission is to support the processes and the regular cycle of strategic planning and operational management of public debt, at different levels of intervention.
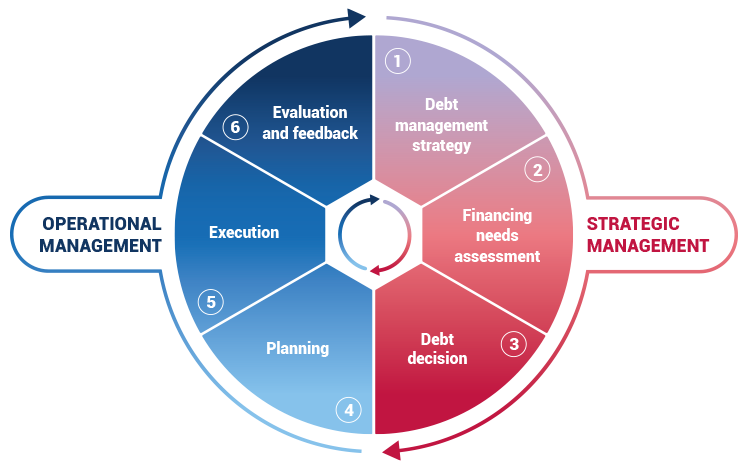
1. DEBT MANAGEMENT STRATEGY
Define risk levels, cost objectives and debt structure
The definition of the strategy for public debt management, in a sustainable way, includes the definition of objectives to be achieved in relation to: minimization of costs; risk limitation; balanced distribution of costs over future years; limitation of the temporal concentration of loan repayment terms.
It also includes the definition of control, information and reporting systems.
2. FINANCING NEEDS ASSESSMENT
Decide how to finance the deficit and investments
The financing needs, to respond to the budget deficit and the investment financing needs for new projects, can be met in several ways. The assessment and characterization of financing needs for decision making is a component of strategic management, framing intervention options, with a view to debt sustainability.
.
3. DEBT MANAGEMENT
Study scenarios, evaluate options and obtain approval of the debt strategy
In order to identify the best indebtedness strategy, among other things, it will be necessary to set up scenarios, evaluate and produce decision elements, taking into account the parameters within which the debt strategy is defined. This will result, based on adequate information, in an implementation decision, in line with the strategy, in terms of maturities, costs and risks.
4. PLANNING
Issurance, amortization and renewal schedule
Taking into account commitments assumed and needs for future indebtedness, as well as the strategic options previously decided, the planning of the necessary actions becomes an act of current management, for the annual execution cycle. Planning consists of the definition and scheduling of management operations, to be carried out, with the necessary rigor, by the various actors in the process, according to their specific function.
5. EXECUTION
Record, analysis and operational reporting (stock, variation, variance analysis)
On a regular basis and on a daily basis, the necessary day-to-day management activities are carried out, based on the plan and according to precise guidelines regarding procedures, means and deadlines. The objective is to ensure transparency and quality in the various interventions, respect for strategic guidelines and regular reporting of monitoring of execution.
6. EVALUATION AND FEEDBACK
Execution evaluation. Lessons learned. Feedback for future cycles.
The evaluation of execution, in the internal and external context in which it was carried out, in the fulfillment of strategic objectives and operational procedures is indispensable for the process of learning and consolidating knowledge. The continuity or alteration of the strategy is based on solid information regarding the fulfillment of the plan and analysis of deviations, complemented with analysis of market trends that allow the identification of emerging risks and formulate scenarios for decision making for future cycles.
PDMS ARQUITECTURE
In order to respond to regular public debt management needs, the functional architecture of the PDMS is characterized by a set of integrated components, easily identifiable in terms of aggregating concepts.
OPERATIONAL MANAGEMENT
It comprises all the functions for current debt registration and management, with a logic of short-term planning, up to one year (but with a focus on future risk), the agenda from which all current operations are initiated and controlled by the various agents in its function.
RELEVANT FEATURES
Operational Planning
- Annual
- Monthly
- Weekly rolling (next days)
Execution
- Registration and validation (Emissions / Disbursements / Refunds)
- Production of alerts
- Maintenance of indicators
- Deviation identification
STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT
It includes the set of functionalities specifically dedicated to the analysis of the future evolution of the debt, to support the strategy framework, analysis of scenarios and the justified selection of the best approach and decisions, at each moment.
RELEVANT FEATURES
Strategic Planning
- Definition of risk levels
- Characterization of the macroeconomic scenario
- Medium-term debt strategy
- Debt sustainability
Analysis/Scenario
- Inclusion of new debt
- Debt composition scenarios
- Deviation simulations (Interest / Currency exchange)
- Amortization/replacement scenarios
- Risk analysis
REPORTING
An aggregate of reporting functionalities, both from an operational and a strategic point of view, to ensure communication and support for decision making.
RELEVANT FEATURES
Operational Reporting
- Current position (stock and commitments)
- Risk elements
- Statistical elements
- Various sectoral analysis
Strategic Reporting
- Evolution scenarios ((Debt composition / MTDS (IMF Medium Term Debt Strategy Framework))
- Risk elements (Interest rates / Exchange rates /Refinancing / State revenue and expenditure)
DEBT DATA
Essential data element, it’s the basis of the entire management process, keeping record of all debt elements (debt stock, internal and external, guarantees) and of all obligations assumed for the future, both internally and externally. It is the central data repository, a key element of debt management, in all its aspects.
INTEGRATION WITH EXTERNAL APPLICATION
The PDMS does not exist in isolation from other information and management systems and needs, for consistency and quality of data and managed information, but also, for reasons of efficiency, effectiveness and risk management. PDMS needs to integrate with the existing application ecosystem, namely, by its integrative characteristic, with the Budget Management System and the Banking System. This aspect needs to be developed / adapted, according to the existing systems to be integrated.